Thirty years ago today, humanity got a chance to see itself in a whole new light.
On Feb. 14, 1990, NASA's Voyager 1 probe snapped a photo of Earth from 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) away. The image shows our home planet as it truly is — a tiny, lonely outpost of life in an incomprehensibly vast cosmos — and became iconic as a result.
The Voyager 1 team sensed at the time that the "Pale Blue Dot," as the photo has come to be known, would be an important social document, said planetary scientist Candy Hansen, who served as the experiment representative for the Voyager imaging team and was the first person to set eyes on the Pale Blue Dot photo when it came down to Earth.
Related: Voyager at 40: 40 photos from NASA's epic 'Grand Tour' mission
The Cold War had not yet thawed completely in early 1990. The Pale Blue Dot had the potential to remind folks around the world that we're all in this together, no matter how many nuclear warheads one superpower may be aiming at another, Hansen explained. And the image remains vital today, because its message is timeless, she added.
"Now, we have climate change as an existential threat," Hansen, who now works for the Arizona-based Planetary Science Institute, told Space.com. "And we need to remind ourselves again that there's one planet that is hospitable to humans. Even if we colonize the moon or Mars one day, neither one of those bodies is really going to be able to support seven billion of us. So, we need to take care of this planet."
A family portrait
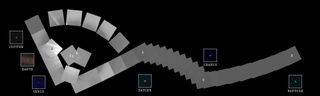
Voyager 1 launched a few weeks after its twin, Voyager 2, back in 1977. Together, the two probes conducted an unprecedented "grand tour" of the solar system's giant planets, flying by Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
The tour was over after the Neptune encounter, which Voyager 2 executed in August 1989. But the two spacecraft kept on flying, out toward the great unknown of interstellar space. Mission team members decided to turn off the two probes' cameras to save precious power during the long journey (and because they probably wouldn't have many chances to photograph interesting things out beyond Neptune anyway).
But Voyager 1 turned around to take one last look at home before closing its eyes. And not just its home planet — its home system. The probe took a "family portrait" series of 60 photos, capturing the sun, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in addition to Earth. (Mercury was too close to the sun to be imaged, and sunlight bouncing around in the camera blocked Mars out.)
The Pale Blue Dot was the brainchild of famed astronomer, science communicator and Voyager imaging team member Carl Sagan, who first proposed snapping Earth with Voyager cameras in 1981. And Sagan helped popularize the image and its message after the fact, writing a book called "Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in Space" (Random House, 1994).
Earth was one of the last things Voyager 1 saw. The probe took the Pale Blue Dot photo at 0448 GMT on Feb. 14, 1990, just 34 minutes before its cameras were shut off forever. (The very last photos Voyager 1 took, however, were of the sun, Hansen said.)
All of the image data didn't come down to Earth until May 1, 1990, NASA officials wrote in a Pale Blue Dot explainer. Hansen couldn't wait to see our planet through Voyager 1's eyes — and, when she finally got the chance, doing so proved a bit more difficult than she had expected.
"It was actually kind of terrifying, because I didn't see it at first," she said. "Because of that beam of scattered light, it didn't pop out at me immediately. And then I was so afraid that we had missed it, or screwed up the exposure or something. So, it was such a relief when I spotted it."
That beam of scattered light may have briefly stopped Hansen's heart, but it adds a certain poetic flair to the Pale Blue Dot photo. It's almost as if the cosmos threw a spotlight onto our precious little world for a moment, to help us make it out in the abyss.
Related: Earth quiz: Do you really know your planet?
Still exploring
Both Voyagers kept flying long after February 1990. They cruised through the outer solar system and eventually popped free of the sun's sphere of influence into interstellar space.
Voyager 1 accomplished this unprecedented feat in 2012, and its twin followed suit six years later. And both probes are still going strong. They should have enough power left to continue gathering data about their exotic surroundings through 2024 or so, mission team members have said.
The Voyager program has accomplished amazing things, shedding considerable light on the giant planets and the dark realms far beyond them. (Voyager 2, for example, is still the only spacecraft ever to get up-close looks at Uranus or Neptune.) And the Pale Blue Dot is a unique part of this diverse and layered legacy.
"The Earth picture reaches to our hearts, I would say, and all the rest goes in our heads," Hansen said.
Mike Wall's book about the search for alien life, "Out There" (Grand Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate), is out now. Follow him on Twitter @michaeldwall. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or Facebook.
https://news.google.com/__i/rss/rd/articles/CBMiSWh0dHBzOi8vd3d3LnNwYWNlLmNvbS9wYWxlLWJsdWUtZG90LXZveWFnZXItMS1waG90by0zMHRoLWFubml2ZXJzYXJ5Lmh0bWzSAU1odHRwczovL3d3dy5zcGFjZS5jb20vYW1wL3BhbGUtYmx1ZS1kb3Qtdm95YWdlci0xLXBob3RvLTMwdGgtYW5uaXZlcnNhcnkuaHRtbA?oc=5
2020-02-14 12:07:00Z
52780605800118
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "Pale Blue Dot at 30: Voyager 1's iconic photo of Earth from space reveals our place in the universe - Space.com"
Post a Comment